What are sanctions?
Sanctions are measures not involving the use of armed force that are imposed in response to a situation of international concern. They aim to limit the adverse consequences of a situation of international concern, impose costs on those responsible, and resolve the situation without the use of force.
Australia enforces two types of sanctions:
- United Nations Security Council (UNSC) sanctions are imposed by the UNSC and Australia is obligated to implement them as a matter of international law
- Australian autonomous sanctions are imposed and implemented by the Australian Government as a matter of Australian foreign policy.
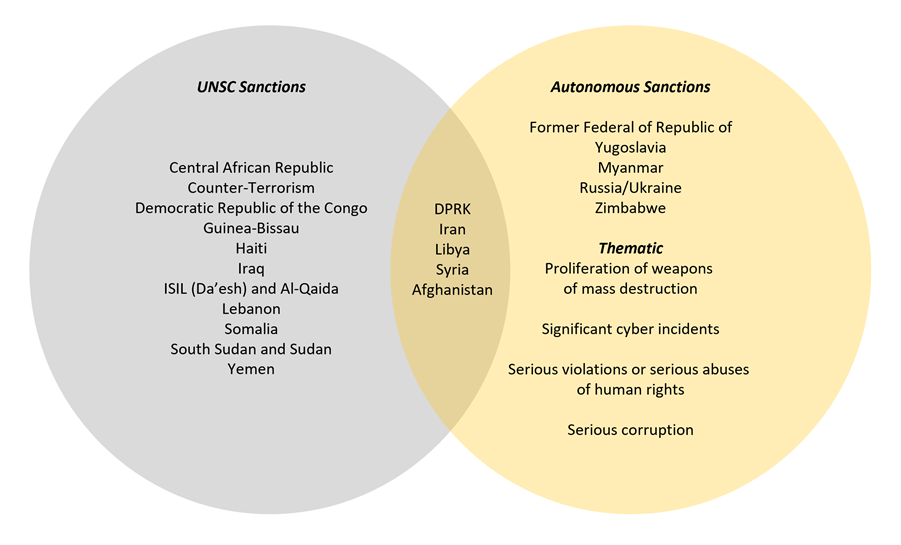
Sanctions imposed in response to a particular situation of international concern are grouped under the sanctions ‘framework’ named after the affected country, group or theme.
The sanctions frameworks currently in effect in Australia
What are sanctions measures?
Each sanctions framework imposes measures, depending on individual circumstances and objectives of the framework. The Charter of the United Nations Act 1945 (Cth), the Autonomous Sanctions Act 2011 (Cth) and regulations made under these Acts use most common terms to describe sanctions measures.
Sanctions measures generally fall into two categories:
- Targeted financial sanctions
- Restrictions on certain goods, services and commercial activities
Other more distinct measures include restrictions regarding vessels under the DPRK and Libya sanctions, dealing with assets of Saddam Hussein's regime, and handling cultural property illegally removed from Iraq and Syria.
Targeted financial sanctions prohibit making assets available to designated persons or entities and dealing with assets owned or controlled by them, effectively freezing these assets. These sanctions may also include travel bans implemented and enforced by the Department of Home Affairs, which prevent designated individuals from entering or transiting through Australia.
Restrictions on certain goods, services and commercial activities generally prohibit the export and/or import of certain goods, the provision of certain services, and engaging in certain commercial activities with specific countries or regions.
The Australian Sanctions Office maintains a Consolidated List of all persons and entities listed for the purposes of sanctions framework implemented under Australian sanctions laws.
Who must comply with sanctions?
Australian sanction laws apply to:
- activities conducted in Australia
- activities conducted overseas by Australian citizens and bodies corporate
- activities conducted on Australian-flagged vessels and aircraft.
In some cases, you may obtain a permit from the Minister for Foreign Affairs to perform activities otherwise prohibited by a sanctions measure. Permit criteria and conditions vary by sanctions framework.
Ministerial Statements of Expectation and Statement of Intent
Commonwealth regulators, including the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trades are accountable to Parliament, including through Senate Estimates and Australian National Audit Office scrutiny.
In addition, Ministers set out their expectations and guidance on how regulators fulfil their statutory roles through Ministerial Statements of Expectations. These Statements are issued by the responsible Minister to a regulator, or an entity with regulatory functions, to provide greater clarity about government policies and objectives relevant to the regulator's statutory objectives and how it conducts its operations.
In response to a Ministerial Statement of Expectations, the regulator issues a Statement of Intent, outlining how it plans to meet the Government's expectations. The Secretary of DFAT has signed a Statement of Intent in response to the Minister's Statement of Expectations, underscoring the Secretary's commitment to ensuring the operations of the Australian Sanctions Office and the Foreign Arrangements Branch align with the Minister's directives and objectives.